The most important parts of a guitar
The most important parts of an electric & acoustic guitar.

In our guitar lessons we often use certain names and terms, or on the internet you can read a discussion about a bridge, nut, headstock, etc … Then it is useful that as a novice guitarist you also know what it is about. Even when playing music together with other musicians, or when you need to order and replace new or worn parts, it is useful to know the correct names of the guitar parts. Because a lot of professional jargon is used in English in the music world, we have always listed the Dutch and English names below.
Headstock : The head stock of the guitar is the outermost part of the guitar neck, where the tuning pegs are located. The headstock is a vulnerable part of a guitar, and when it lands or falls incorrectly, it sometimes breaks where the nut is. The headstock also has a lot of force and pressure due to the tension of the strings. To absorb this force, the head is often glued to the neck at a certain angle, with this angle differing according to brand and type of guitar.
Tuning Pegs (tuning screw, tuning knob, tuners mechanism) : The tuning peg is a mechanism around which the string is wound. The string is fastened here and finely or coarsely tuned (some guitars still have fine tuning on the bridge). Depending on the guitar model, the tuning screws are at the top, bottom (guitars without headstock like e.g. Steinberg), or on both sides (e.g. Ibanez with Floyd Rose system).
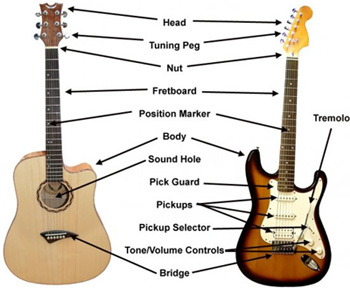
Nut : The nut of the guitar neck is the piece of plastic, bone, graphite or brass, over which the strings run to the headstock of the guitar. Playability in the lower positions depends mainly on the height of the nut. The lower, the better. The ideal nut is as high as the first fret. That is why you see on some guitars a so-called nulfret. Combs can be made of different materials, but the main problem is that there is friction between the string and the nut, which can cause the string to stick during tuning. There are several solutions for this, including : filing out the comb, a comb with ball bearings, a locking nut like eg Ibanez, lubricating graphite in the slots of the comb.
Neck (guitar neck) : The neck of the guitar is the part between the headstock and the body, where the frets are mounted. The shape of the neck and the distance between the frets and the strings (action, action) determine the ease of playing a guitar. The ideal action depends on personal taste, and on the style of music. For metal, a low action is more likely to be used, for funk (with a more aggressive attack) a higher action is recommended to avoid rattling of the strings. But generally speaking, if the action is low and thus the strings are close to the frets, a guitar is easier to play because there is less pushing force to be put on the strings. The neck is often made of mahogany or maple. The fingerboard (fretboard) is often made of rosewood, ebony or maple.
Fretboard (fingerboard) : The fretboard is the part that holds the frets in place. Often the fretboard is another type of wood glued on top of the guitar neck and is made of rosewood, maple or ebony among others.
Frets : Frets are the metal strips that run across the fretboard of the neck. They are made of an alloy consisting of 18% nickel, 55% copper and 27% zinc. This alloy has a certain, not too high, degree of hardness, which causes the frets to wear out (called fretwear). In that case, the frets have to be replaced, which is a very delicate and expensive job. There are different sizes of frets including small, medium, narrow, jumbo, etc where both the height and width can vary.
Body : The largest part of the guitar is the body. Guitar bodies come in different sizes and shapes. The body (acoustic) or the body (electric) largely determines how a guitar sounds. Wood types play an important role here, but even more important is how the guitar is made. The most ideal body of a guitar, are those with a more ergonomic shape. Special guitars like a Flying V, double neck or Bo Diddley Gretsch are pretty cool, but are very awkward and impractical. Those are ideal guitars to . hang against your wall
Electronics : On the bottom we have Pickups, Pickup Selector Switch, Input Jack and Knobs. With guitars and basses you will find the most diverse electronic schemes, from a simple scheme with volume potentiometer to built-in preamplifier and active controls. Moving (mechanical) parts of the electronics wear out the fastest, such as the jack input and switch pickup selector.
Pickups (elements) : The pickups on the guitar are magnetic microphones/elements. Depending on the guitar model, there may be 1, 2 or even three pickups present. There are both single coil and double coil elements for the electric guitar (single coil pickups, double coils / humbuckers). The humbucker has two coils with magnets connected side by side in series where the magnets are opposite in polarity and one coil is also wound oppositely. Humbuckers are especially suitable for a solid rock sound and sound warmer than a single-coil element. Single coil elements, on the other hand, give that specific Fender Stratocaster sound, sounding thinner and more shrill. Nowadays there are double coil pickups that can switch to a single coil pickup via a push-pull switch. For example, a guitar with heavy sound can suddenly be switched to a meet strat-like sound.
Pickup Selector Switch (element switch) : The pickup selector switch is used to choose which pickup or pickups are used. Depending on the number of pickups, this can be a 3 or 5 way switch.
Input Jack : Where one has to plug the guitar cable into an electric or acoustic guitar that is the input jack. It sometimes happens that this input jack starts to unload where the cable starts to crack or causes dropouts (signal loss). In that case, the input jack must be carefully screwed on.
Knobs (potentiometers) : The knobs on a guitar exist in different configurations, but usually have 2 basic functions: volume and tone. A volume knob speaks for itself, the tone knob provides more or less treble (treble, shrill and sharper sound versus duller sound). There are also push-pull potentiometers that have a double function, which e.g. serve as a switch between single and double coil function of a pickup, or to activate a built-in booster or pre-amp for a higher output.
Bridge : The bridge is mounted or glued to the body of the guitar, to which the strings are attached. For electric guitar there are many different bridges, but in general there are the stoptails, tremolos and tune-o-matic bridges.

